EMC temperature test chamber – Shielding with temperature
The EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) is a temperature test chamber equipped with optimal shielding attenuation: VT 4021 / 7021 EMC, EMC Minis - VT 4002 EMC.

Electromagnetic compatibility
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is defined as the ability of an electric device to function satisfactorily within its electromagnetic environment (interference resistance). This must function without unduly affecting this environment which itself contains other devices (emitted interference).
Electromagnetic influences can result in malfunctions of electrical de- vices and systems (e.g. aircraft, car, railway, ship, etc.). The technical measurement of the electromagnetic compatibility of a system and appropriate protection measures for reduction or suppression of the electromagnetic interference are the subject of numerous research projects.
The correct layout and the design are crucial for the EMC behavior. Proof and confirmation of interference immunity and sufficiently low interference emission are regulated by EMC Directives and EMC standards (IEC 61000-5-7-2001).
Protection requirements specify that interference emissions of the test specimen must be so low that, e.g. radio receivers etc. in the environment are not unduly affected.
Test Equipment
Limited laboratory area and the need to test directly at the work place re-requires compact and quiet devices.
Vötsch Industrietechnik has developed standard devices which are equipped with optimal shielding attenuation. The shielding attenuation was measured and certified by the Institute for Electric Energy Systems and High-Voltage Engineering (EH) of the University of Karlsruhe (TH).
The test space is designed so that the interior container takes over a shield function. The shield attenuation (SA) specifies the ability of an electromagnetic shield to reduce or attenuate electromagnetic fields and surface currents.
The electro-magnetic protection (EM protection) is provided by the complete topology (structure). This consists not only of the metallic shell but includes electric lead-throughs (current, communication, antenna, signal cables) and mechanical lead-throughs (door, tubes, connector panel etc.).
Aim of a temperature test in a shielded system is the proof of the resistance of a test specimen to an electromagnetically shielded environment at various reproducible temperatures.
The investigation is aimed at checking the suitability for operation and storage at low and high temperatures.
The functional capability and serviceability of a product are already ensured at a very early stage in the research and development laboratory.
With this series, we are providing the developer and quality assurance an excellent effective electromagnetic shield in combination with the established controlled temperature test chambers.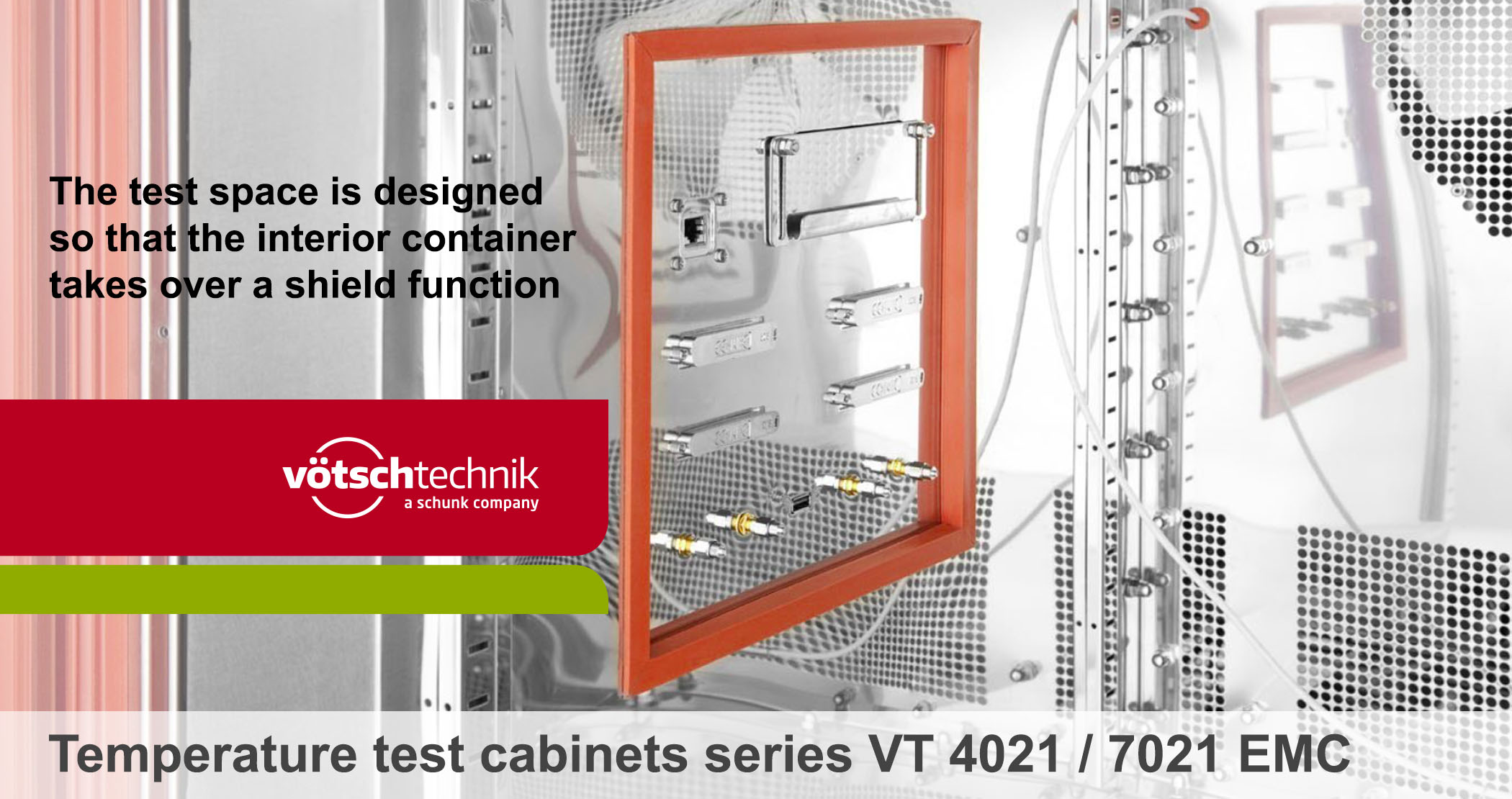
VT 4021 / 7021 EMC
The temperature test cabinets series VT 4021 / 7021 EMC are equipped with optimal shielding attenuation with a test space volume of approx. 200 litre and a temperature range from -35°C / -65°C to 100°C.

EMC Minis - VT 4002 EMC
The VT 4002 EMC is a miniature temperature test chamber equipped with optimal shielding attenuation. The test space is designed so that the interior container takes over a shield function.
The shielding attenuation was measured and certified by the Institute for Electric Energy Systems and High-Voltage Engineering (EH) of the University of Karlsruhe (TH).
Features
- EM-Code xxx55*x / *) up to 3 GHz,
- For monitoring and controlling the test chamber is equipped with a powerful 32-bit control system SIMPAC,
- The touch panel offers input and display of values and states,
- Extremely quiet.
The electromagnetic protection (EM protection) is provided by the complete topology (structure).
This consists of:
- The metallic shell,
- Electric lead-throughs (current, communication, antenna, signal cables),
- Mechanical lead-throughs (door, tubes, connector panel etc.).
























